Overview of GST Registration
GST Registration is one of the very important business compliance nowadays. Businesses with a turnover of more than Rs 20 lakhs (10 lakhs in the North East and hill states) must register for GST as a normal taxable person as per the new GST regulation. Apart from the various turnover brackets, there are other instances where getting a new GST registration online is required for people or companies engaged in the provision of goods or services across the state. It is a mandatory requirement of the businesses and one cannot ignore it. Ignorance of this compliance can attract heavy penalties and fines because as per GST Act it is an offense. Such kinds of penalties can prove fatal for one business. Hence every businessman who wants to escape from such fines and penalties must take GST Registration. The process of getting this registration is fully online, but it does not mean it's easy to get such registration. Therefore expert advice is always suggested.
What is GST?
GST which stands for Goods and Services Tax was implemented in India with the goal of eliminating various indirect taxes like exercise duty tax, service tax, purchase tax, etc. It established a single taxation structure for the whole of India. GST will be applied to both products and services, as part of a dual system of GST that separates the duties of the federal and state governments. The GST Council will be chaired by the Union Finance Minister and would include representatives from various state finance departments. GST also facilitates the collection and improves the efficiency of the process. Before GST central and state government has different kinds of taxes but now for the whole of India, there is just one tax which is GST.
Modes of GST in India-
There are four modes of GST in India, which define different levels of GST. They are on the basis of national level, state level, an integrated level, and union territories level. Given below is the detail of all of them.
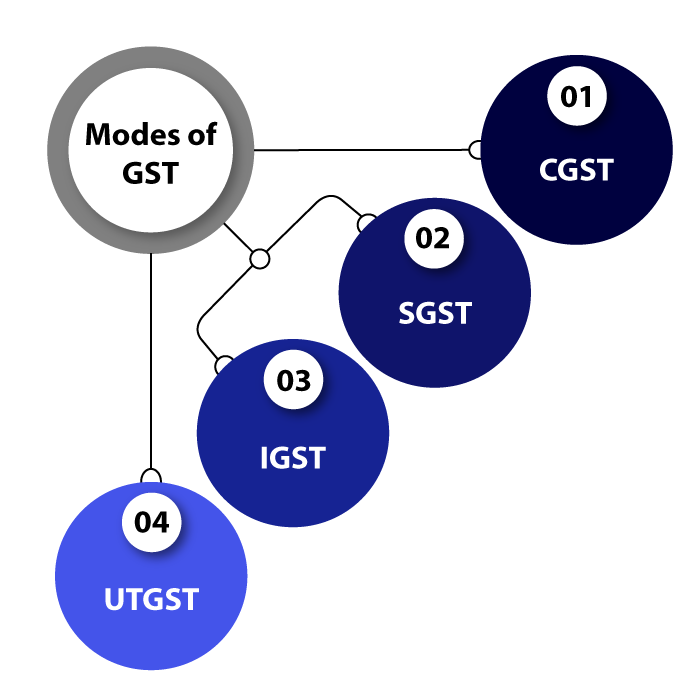
GST at the national level (Central GST)
The Central Government levies a tax on intra-state deliveries of goods and services, known as the CGST. An intra-state supply of products or services occurs when the seller and buyer are both located in the same state. A seller must collect both CGST and SGST in this case, where the CGST is for central government and the SGST is for state government.
GST levied by the state (State GST)The SGST is a tax levied by the state government on intra-state deliveries of goods and services.
GST that is integrated (Integrated GST)
The IGST Act governs Integrated GST, which requires sellers to collect IGST from buyers and divide the tax collected between the federal and state governments.
GST in the Union Territories (Union Territory GST)
When products and services are utilized in India's Union Territories (UTs) and revenue is collected by the government of the union territory, it is referred to as Union Territory GST.
Constituents of the GST-
What is the GST structure of slabs?
GST regimes were created with the average person in mind, as well as inflation rates. The GST was designed in a four-tiered structure to make it simpler and easier to understand. These four zones are listed below-
- The term "zero rate tax" refers to the application of no tax on products and/or services.
- The 5 percent tax rate is determined by the lower tax rate, which is applied to the CPI basket and mass consumption.
- The standard rate includes tax rates of 12 percent and 18 percent.
- Under the GST Regulation, the higher rates tax includes a tax rate of 28%.
History of the GST-
Implementation of GST is a very long process. It is a big change in the economy of India. The government almost took 17 years the implementation the GST. It was a big change and it’s not easy to implement such changes and that is one of the reasons a very long time has been taken for the implementation of the GST. Following is the list which is depicted the history of the GST-
- In 2000 a committee was set up will draft the GST Law.
- In the years 2004, it was proposed by the task force that a new task structure should be there which will enhance the tax regime.
- In 2006 it was proposed that a new tax structure that is GST will be introduced in the year 2010.
- In 2011 constitutional amendment will be passed which will enable the introduction of the GST Law.
- 2012 was the year when the standing committee started talking about the GST and stated that “GST a year later”.
- In 2014 a new GST bill was introduced in the parliament.
- Lok Sabha passed the bill in the year 2015.
- In 2016 GST Law became live after got passed by both the houses of the parliament and also got the president assent.
- Finally on the 1st of July 2017 we got the Goods and Services Tax.
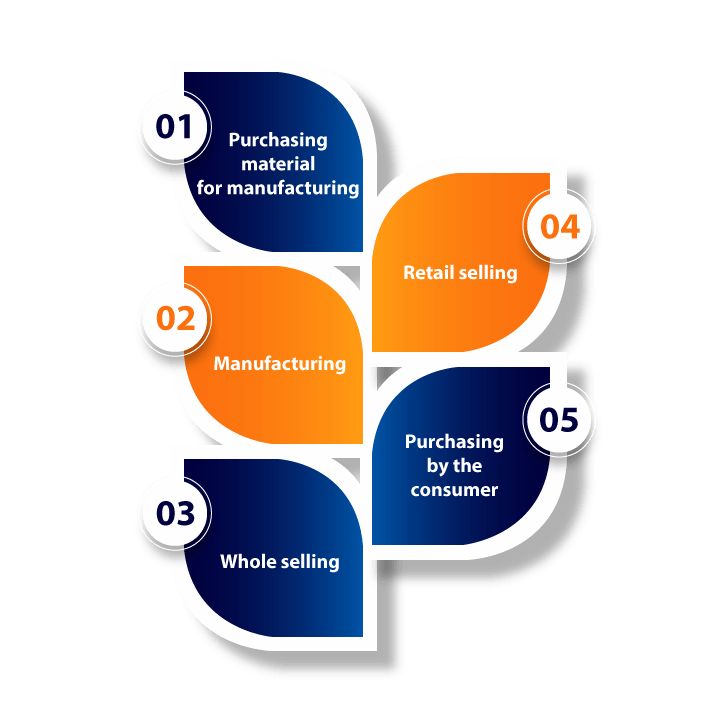
Stages when GST levied-
Every goods and services goes through various stages before coming into the hands of the consumer. The various stages are manufacturing, whole selling, retail selling, and then after passing all these stages product or service came into the consumer’s hand. In short, there are five stages purchasing, manufacturing, whole selling, retail selling, and finally consumer purchase it for his or her use. GST is levied on all five stages separately.
What is GST Registration?
The process of registering a taxpayer under the Goods and Services Act is called GST registration. It is an online process that has to complete through the government GST Portal. After the completion of the registration, the taxpayer will get the registration number through which he has to pay GST Tax.
Benefits of the GST Registration-
There is lots of benefit of the above-mentioned registration, out of which some most important are discussed below-
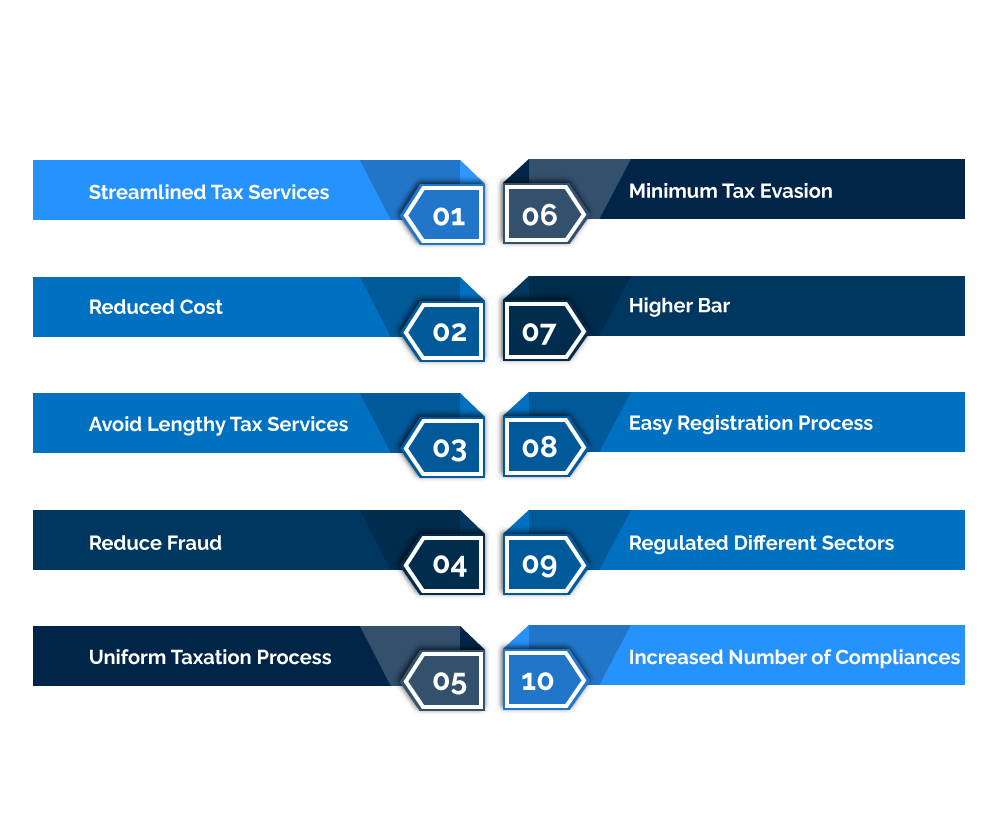
Taxation Services are streamlined
GST has brought together a lot of indirect taxes under one roof, allowing the Indian market to become more integrated.
Costs of goods and services are being reduced.The cascading impact of a variety of VATs and taxes was eliminated with the introduction of GST, resulting in a reduction in the cost of goods and services.
Allows you to avoid lengthy tax servicesSmall enterprises can avoid lengthy taxation services by registering for GST. Service providers with a turnover of fewer than 20 lakhs and products providers with a turnover of fewer than 40 lakhs are not required to pay GST.
Designed to reduce fraud and sales without receiptsThe purpose of the GST was to reduce corruption and sales without receipts. It also makes it easier for small businesses to deal with numerous indirect taxes.
Taxation Process UniformityGST registration gives taxes procedure standardization and enables centralized registration. This makes it easier for businesses to complete tax forms online every quarter.
Keeping Tax Evasion to a MinimumTax evasion has been greatly reduced with the implementation of the GST.
Registration Requires a Higher BarPreviously, any business with a turnover of more than Rs 5 lakh was required to pay VAT in India under the VAT system. In addition, service providers having a turnover of less than Rs 10 lakh are free from paying service tax. On the other hand, under the GST regime, this barrier has been raised to Rs 20 lakh, exempting a large number of small traders and service providers.
Online Procedure That Is Simple and EasyThe entire GST process (from registration to submitting returns) is completed online and is extremely straightforward. This has mostly benefited start-ups, as they no longer have to run from pillar to post in order to obtain various registrations such as VAT, excise, and service tax.
The Number of Compliances Is DecreasingPreviously, there existed VAT and service tax, each with its own set of returns and requirements. In the case of GST, however, there is only one unified return to file.
Unorganized Sector RegulationsCertain industries in India, like as construction and textiles, were primarily unorganized and unregulated prior to the introduction of the GST. However, under GST, there are facilities for online compliance and payments, as well as the ability to claim input credit only once the supplier has received the amount. These industries are now more accountable and regulated as a result of this.
GST Registration and small business owners-
GST Composition Scheme is for small businesses, which do not have high turnover. Compliances are less under Composition Scheme when compared with normal GST Compliances. The purpose of this scheme is to promote ease of doing business. The tax rates under Composition Scheme are very less in comparison to normal GST rates. This scheme will be applicable intrastate. This can be opted only by the person who will fulfill its criteria. There are fewer formalities under this scheme in comparison to normal GST formalities. It will definitely reduce the unnecessary burden of high taxes on small business holders. In short, we can say that this scheme is a helping hand of the government toward small businesses.
What is GST Return under Composition Scheme?
GST Return under Composition Scheme is a government filing that needs to be done annually. Through GST Return filing government asses your business which helps the government in many different ways. Such as making future policies, collecting financial data, doing different surveys, etc. GST Return filing under Composition Scheme is a source of government that provides information about the sales of any business. It is an obligation of return filing compliance which saves the filer from heavy penalties.
Eligibility criteria for GST Registration in India-
There are certain eligibility criteria to get GST Registration, some of them has been discussed below-
Documents required for GST Registration in India-
The type of business determines which documents are necessary for Online GST Registration. The following are the lists of documents required for GST registration (depending on the type of business): -
- For a sole proprietorship business.
- The owner's PAN card
- The owner's Aadhar card.
- The owner's photo (in JPEG format, maximum size - 100 KB).
- Details of your bank account.
- Proof of address is required.
For a partnership firm
- All partners' PAN cards are required (including managing partner and authorized signatory).
- A copy of the collaboration agreement.
- All partners and authorized signatures (in JPEG format, maximum size – 100 KB) must be photographed.
- Proof of partners' addresses (Passport, driving license, Voters identity card, Aadhar card, etc.).
- Authorized signatory's Aadhar card
- Proof of the authorized signatory's appointment.
- Registration certificate / LLP Board resolution in the case of an LLP.
- Details of your bank account.
- Proof of the major place of business's address.
For a HUF
- You'll need a HUF PAN Card and a passport-sized photograph of the Karta.
- Karta's ID and address evidence, as well as the address evidence of the business.
- Details of your bank account
For a Public or Private Limited Company
- The company's pan card is required.
- Company's certificate of incorporation.
- The company's MOA and AOA.
- All directors and authorized signatory of the company must provide proof of identity and address.
- Photographs of the directors and authorized signatories at passport size.
- A copy of the board resolution naming an authorized signatory.
- Details on how to open a bank account.
- Proof of the company location's address.
Procedure to get GST Registration in India-
To complete the GST registration procedure successfully, each taxpayer must follow the steps given below-
- Applicant has to complete the online application given on the government GST Portal.
- Generate a username and password.
- The applicant should go to the GST site and log in.
- Fill in the information and upload all the documents needed.
- Input the OTP supplied to your email address and mobile number in the appropriate fields.
- On the screen, an applicant will be given a Temporary Reference Number (TRN). After receiving the TRN, an applicant must reopen the GST portal and select "Register" from the "Taxpayers" option.
- Fill in the TRN and captcha information.
- Submit the form.
- Verification will be done by the appropriate authority.
- After valid verification you will get the registration.
Validity of the GST Registration Certificate-
The sort of taxpayer who receives a GST registration certificate determines and conditions the validity of the certificate. When an ordinary taxpayer receives a certificate, it is valid for life. It only becomes invalid in such instances if the GST authority cancels it or the taxpayer surrenders it. In circumstances where certificates are granted for casual taxpayers or Non-Resident Indian (NRI) taxpayers, the validity is limited to 90 days from the date of registration or the term mentioned in the registration application, whichever comes first. The validity term can also be extended by the authorized authorities under the terms of Section 27(1) of the GST Act.
Why Taxsavio?
Taxsavio is one of the many platforms which coordinate to fulfill all your legal requirements. It is a legal service platform that is running on cloud-based technology. It connects you with a team of expert professionals who can help you in every possible way. Its focus is on simplifying the legal requirements for the client. If you have any questions regarding GST Registration we are just one phone call away. We have a very dedicated team that is ready to help you and guide you. Our mission is to create a hustle-free and easy-to-use system for the concerned consumers of our services. We give you reliability and trust. We make sure that we will provide you with the best services and can satisfy you with our quality work.
Conclusion-
Although GST Registration is an online process it does not mean it is piece of cake and anybody can do this. It includes many technicalities which are not at all easy to do. Hence expert help should be taken while registering for GST.GST included in the final price of all goods and services before they are purchased, and it eliminates all indirect taxes that were previously imposed by the central government and state governments in India. This concept of GST was started in India in 2017. It makes the work easy and less hectic for the government by proving uniformity.
Frequently Asked Questions
GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. It is an indirect tax that is levied on all goods and services. It makes the work easy and eliminates many taxes which had to be paid before GST.
The process of registering a taxpayer under the Goods and Services Act is called GST registration.
One can be registered for GST by visiting the online GST Portal of the government. The full procedure for obtaining registration is given below-
- Fill out the online form.
- Upload all the documents and information they are asking for.
- Pay the required fees and generate the challan.
- Verification will be done by the appropriate authority.
- After valid verification, you will get the registration certificate.
Only those businesses whose turnover is more than Rs 20 lakhs (10 lakhs in the North East and hill states) must register for GST as a normal taxable person as per the new GST regulation.
- Normal Taxpayer
- Casual Taxable Person
- Composition Taxpayer
- Non-Resident Taxable Person
 9899615888
9899615888 9899615888
9899615888 9899615888
9899615888
